| Cost
Control: Inside the Oracle Optimizer
By Donald K. Burleson
Designing
new applications for the Oracle Cost-Based Optimizer?
Here's the latest information about how it works. |
|
|
The goal of SQL tuning is to execute your SQL with the absolute
minimum amount of I/O. See my related SQL Optimization tips at
the end this article.
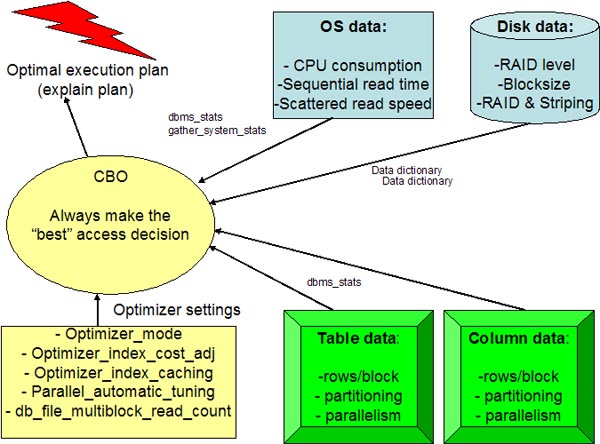
Oracle's cost-based SQL optimizer (CBO) is
an extremely sophisticated component of Oracle that governs the
execution for every Oracle query. The CBO has evolved into one of the
world's most sophisticated software components, and it has the
challenging job of evaluating any SQL statement and generating the "best" execution plan for the statement.
Because the CBO determines the execution
speed for every Oracle query, the Oracle professional must understand
how the CBO is influenced by Oracle external issues, internal
statistics, and data distribution.
In this first installment of a two-part
article, we will cover the following CBO topics:
- CBO parameters. We will
start by reviewing the basic optimizer modes within the CBO and then drill down and examine specific parameters that influence the
behavior of the CBO.
- CBO statistics. We will
examine the importance of gathering proper CBO statistics with
dbms_stats and review
techniques for ensuring that execution plans remain stable. We will
also look at techniques for migrating statistics between systems and
examine how developers can optimize their
SQL in a test environment
and confidently migrate SQL into production without fear of changing execution plans.
This article has the following sections:
What's new in
Oracle Database 10g?
With the advent of Oracle Database 10g
we now see dramatic internal improvement to the cost-based SQL
optimizer and easier mechanisms for automatic SQL optimization. The
important SQL optimizer changes to Oracle Database 10g include
the following exciting topics:
- Rule-based optimizer de-support
— While the rules-based optimizer (RBO) exists inside Oracle
Database 10g, Oracle highly recommends that those using
rule-based optimization procrastinate no longer. Those sites that
are still using the RBO can switch to first_rows
optimizer_mode and adjust the parameter
optimizer_index_cost_adj to a small
number (< 25) to make the cost-based optimizer simulate the behavior
of the RBO. Shops that do not want their Oracle Database 10g
migration to change their execution plans can use Oracle's optimizer
plan stability feature to preserve their rule-based execution plans
prior to migrating.
- User-Initiated Buffer Cache
Flushing — You can now flush the buffer cache manually between
runs of test queries, which facilitates your diagnosing and testing
of SQL run-time execution. For SQL unit testing, this ability to
clear the data buffers ensures uniform SQL response time testing and
removes the performance variability associated with RAM data
caching.
- SQLAccess Advisor — The
SQLAccess Advisor is an expert system inside the
dbms_advisor package that
identifies (and advises on resolution) of SQL execution performance
problems. It analyzes SQL from the library cache and recommends
which indexes or materialized views to create, drop, or retain.
Cost Basis
While we have gone into great detail on the
optimizer, there is always more to learn as the optimizer becomes more
powerful (and complex) with each new release. The main points of this
article include general guidelines for adjusting the behavior of the
optimizer:
- Histograms provide detailed column
information to the optimizer in rare cases when the value of an
index column would change the optimal execution plan. Hence,
histograms should be used only when justified.
- Writing SQL that gets the correct
data is not enough. Developers should be held responsible for tuning
their SQL and should be trained in optimal SQL formatting and
understand how to use explain plan
and TKPROF.
- The most common problems with SQL
optimization are missing indexes (or non-selective indexes) and
sub-optimal table join methods.
- Oracle hints are used to change
execution plans for a query, but should only be used as a last
resort.
- The v$sql_plan
view shows the execution plan for all SQL in your library cache and
you can query this view to get useful insights into SQL execution
internals.
Special thanks to Oracle SQL Guru
Andrew Holdsworth for his assistance.
Oracle 11g Notes
Even though Oracle has deprecated the rule-based optimizer, Oracle
continues to use the rule hint in Oracle 11g, as shown by this Data
Pump internal SQL:
Module: Data Pump Worker
SELECT /*+rule*/
SYS_XMLGEN(VALUE(KU$),XMLFORMAT.createFormat2(
'TABLE_T', '7')),
KU$.OBJ_NUM ,KU$.ANC_OBJ.NAME . . .
My related notes on Oracle SQL optimization:
 |
|
Get the Complete
Oracle SQL Tuning Information
The landmark book
"Advanced Oracle
SQL Tuning The Definitive Reference" is
filled with valuable information on Oracle SQL Tuning.
This book includes scripts and tools to hypercharge Oracle 11g
performance and you can
buy it
for 30% off directly from the publisher.
|
|