| Cost
Control: Inside the Oracle Optimizer
By Donald K. Burleson
|
|
|
This article has the following sections:
PART 7 - Using Hints to Change Execution Plans
As the optimizer becomes more sophisticated
with each release, Oracle provides an increasing number of methods for
changing the execution plans for your SQL. The most common use for
Oracle hints is as a debugging tool. You can use the
hints to determine the optimal execution plan, and then work backward, adjusting the statistics to make the vanilla SQL simulate the hinted
query.
Using Oracle hints can be very complicated
and Oracle developers only use hints as a last resort, preferring to alter the statistics to change the execution plan. Oracle contains
more than 124 hints, and many of them are not found in the Oracle
documentation. (See
Listing 2)
Listing 2: Documented Oracle Hints:
ALL_ROWS
AND_EQUAL
ANTIJOIN
APPEND
BITMAP
BUFFER
BYPASS_RECURSIVE_CHECK
BYPASS_UJVC
CACHE
CACHE_CB
CACHE_TEMP_TABLE
CARDINALITY
CHOOSE
CIV_GB
COLLECTIONS_GET_REFS
CPU_COSTING
CUBE_GB
CURSOR_SHARING_EXACT
DEREF_NO_REWRITE
DML_UPDATE
DOMAIN_INDEX_NO_SORT
DOMAIN_INDEX_SORT
DRIVING_SITE
DYNAMIC_SAMPLING
DYNAMIC_SAMPLING_EST_CDN
EXPAND_GSET_TO_UNION
FACT
FIRST_ROWS
FORCE_SAMPLE_BLOCK
FULL
GBY_CONC_ROLLUP
GLOBAL_TABLE_HINTS
HASH
HASH_AJ
HASH_SJ
HWM_BROKERED
IGNORE_ON_CLAUSE
IGNORE_WHERE_CLAUSE
INDEX_ASC
INDEX_COMBINE
INDEX_DESC
INDEX_FFS
INDEX_JOIN
INDEX_RRS
INDEX_SS
|
INDEX_SS_ASC
INDEX_SS_DESC
INLINE
LEADING
LIKE_EXPAND
LOCAL_INDEXESMATERIALIZE
MERGE
MERGE_AJ
MERGE_SJ
MV_MERGE
NESTED_TABLE_GET_REFS
NESTED_TABLE_SET_REFS
NESTED_TABLE_SET_SETID
NL_AJ
NL_SJ
NO_ACCESS
NO_BUFFER
NO_EXPAND
NO_EXPAND_GSET_TO_UNION
NO_FACT
NO_FILTERING
NO_INDEX
NO_MERGE
NO_MONITORING
NO_ORDER_ROLLUPS
NO_PRUNE_GSETS
NO_PUSH_PRED
NO_PUSH_SUBQ
NO_QKN_BUFF
NO_SEMIJOIN
NO_STATS_GSETS
NO_UNNEST
NOAPPEND
NOCACHE
NOCPU_COSTING
NOPARALLEL
NOPARALLEL_INDEX
NOREWRITE
OR_EXPAND
ORDERED
ORDERED_PREDICATES
OVERFLOW_NOMOVE |
PARALLEL
PARALLEL_INDEX
PIV_GB
PIV_SSF
PQ_DISTRIBUTE
PQ_MAP
PQ_NOMAP
PUSH_PRED
PUSH_SUBQ
REMOTE_MAPPED
RESTORE_AS_INTERVALS
REWRITE
RULE
SAVE_AS_INTERVALS
SCN_ASCENDING
SELECTIVITY
SEMIJOIN
SEMIJOIN_DRIVER
SKIP_EXT_OPTIMIZER
SQLLDR
STAR
STAR_TRANSFORMATION
SWAP_JOIN_INPUTS
SYS_DL_CURSOR
SYS_PARALLEL_TXN
SYS_RID_ORDER
TIV_GB
TIV_SSF
UNNEST
USE_ANTI
USE_CONCAT
USE_HASH
USE_MERGE
USE_NL
USE_SEMI
USE_TTT_FOR_GSETS |
Undocumented Hints:
BYPASS_RECURSIVE_CHECK
BYPASS_UJVC
CACHE_CB
CACHE_TEMP_TABLE
CIV_GB
COLLECTIONS_GET_REFS
CUBE_GB
CURSOR_SHARING_EXACT
DEREF_NO_REWRITE
DML_UPDATE
DOMAIN_INDEX_NO_SORT
DOMAIN_INDEX_SORT
DYNAMIC_SAMPLING
DYNAMIC_SAMPLING_EST_CDN
EXPAND_GSET_TO_UNION
FORCE_SAMPLE_BLOCK
GBY_CONC_ROLLUP
GLOBAL_TABLE_HINTS
HWM_BROKERED
|
IGNORE_ON_CLAUSE
IGNORE_WHERE_CLAUSE
INDEX_RRS
INDEX_SS
INDEX_SS_ASC
INDEX_SS_DESC
LIKE_EXPAND
LOCAL_INDEXES
MV_MERGE
NESTED_TABLE_GET_REFS
NESTED_TABLE_SET_REFS
NESTED_TABLE_SET_SETID
NO_EXPAND_GSET_TO_UNION
NO_FACT
NO_FILTERING
NO_ORDER_ROLLUPS
NO_PRUNE_GSETS
NO_STATS_GSETS
NO_UNNEST
NOCPU_COSTING |
OVERFLOW_NOMOVE
PIV_GB
PIV_SSF
PQ_MAP
PQ_NOMAP
REMOTE_MAPPED
RESTORE_AS_INTERVALS
SAVE_AS_INTERVALS
SCN_ASCENDING
SKIP_EXT_OPTIMIZER
SQLLDR
SYS_DL_CURSOR
SYS_PARALLEL_TXN
SYS_RID_ORDER
TIV_GB
TIV_SSF
UNNEST
USE_TTT_FOR_GSETS |
|
Let's take a quick look at how hints are
used to alter optimizer execution plans: A optimizer hint is an optimizer directive placed inside comments inside your SQL statement
and used in those rare cases where the optimizer makes an incorrect decision about the execution plan.
Because hints are inside comments, it is important to ensure that the
hint name is spelled correctly and that the hint is appropriate to the
query.
The all_rows optimizer mode is designed to minimize computing
resources and it favors full-table scans. Index access
(first_rows) adds additional I/O overhead, but they return rows
faster, back to the originating query:
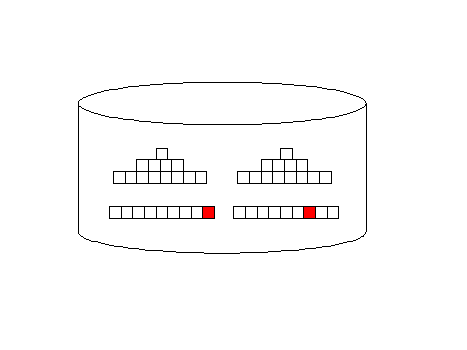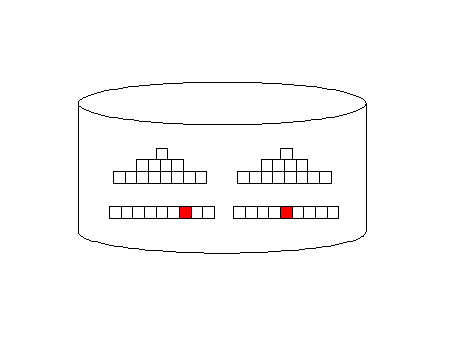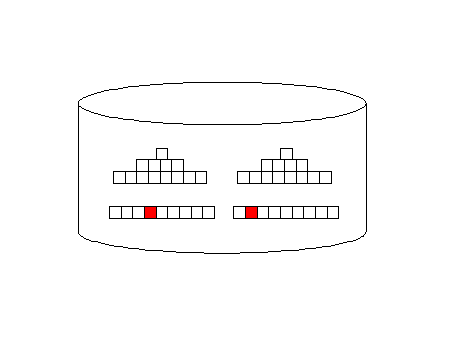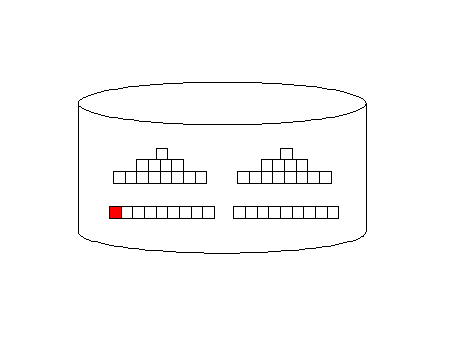
Oracle full-table scan
Illustration
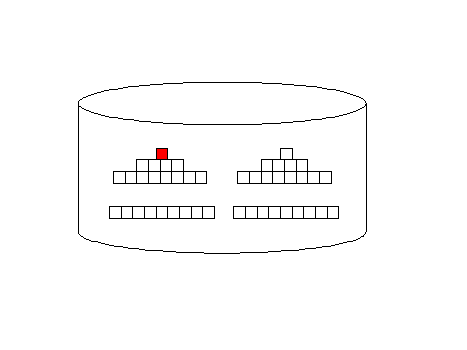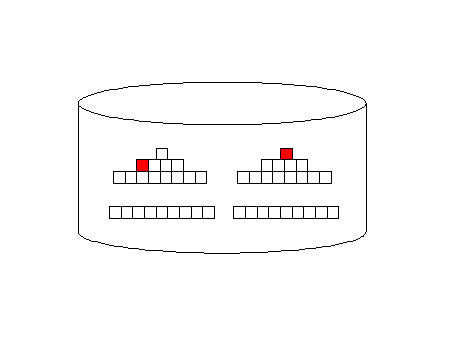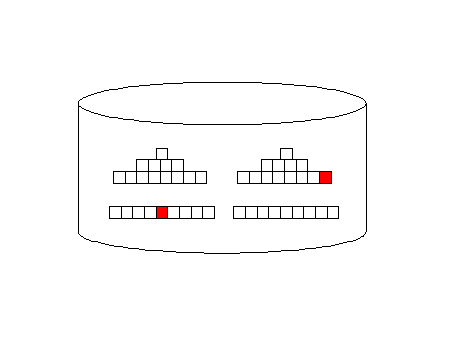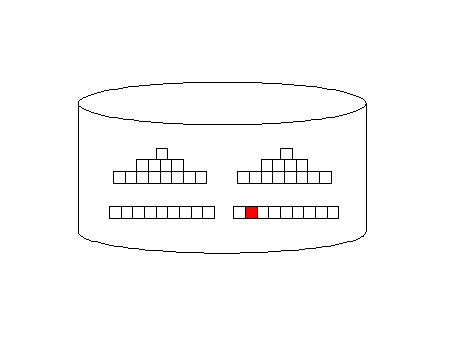
Oracle Index
access illustration
For example, the following hint is invalid
because first_rows_n access and
parallel access are mutually exclusive. That's
because parallel always assumes
a full-table scan and first_rows_n
favors index access.
-- An invalid hint
select /*+ first_rows_100 parallel(emp,8)*/
emp_name
from
emp
order by
ename;
Some Oracle professionals will place hints
together to reinforce their wishes. For example, if we have an SMP server with eight or more CPUs, we may want to use Oracle Parallel
Query to speed-up legitimate
full-table scans. When using parallel query, we seldom want to turn-on
parallelism at the table level (alter table customer parallel 35;) because the setting of parallelism for a
table influences the optimizer, causing the optimizer to see
full-table scan is inexpensive. Hence, most Oracle professionals
specify parallel query on a query-by-query basis,
combining the full hint with the parallel
hint to ensure a fast parallel full-table scan:
-- A valid hint
select /*+ full(emp) parallel(emp,35)*/
emp_name
from
emp
order by
ename;
Now that we have the general concept of
hints, let's take a look at one of the most important hints for optimizer tuning.
The ordered
hint determines the driving table for the query execution and also
specifies the order that tables are joined
together. The ordered hint
requests that the tables should be joined in the order that they are specified in the from clause,
with the first table in the from
clause specifying the driving table. Using the ordered hint can save a huge amount of
parse time and speed SQL execution because you are telling the
optimizer the best order to join the tables.
For example, the following query uses the
ordered hint to join the tables in their specified order in the
from clause. In this
example, we further refine the execution plan by specifying that the emp to dept join use a hash join and the sal to
bonus join use a nested loop join:
select
/*+ ordered use_hash (emp, dept) use_nl (sal, bon) */
from
emp,
dept,
sal,
bon
where . . .
Of course, the ordered
hint is most commonly used in data warehouse queries or in SQL that
joins more than five tables.
Our preferred SQL tuning tool:

Our Ion tool is
the easiest way to analyze Oracle SQL performance and Ion
allows you to spot hidden SQL performance trends.
 |
|
Get the Complete
Oracle SQL Tuning Information
The landmark book
"Advanced Oracle
SQL Tuning The Definitive Reference" is
filled with valuable information on Oracle SQL Tuning.
This book includes scripts and tools to hypercharge Oracle 11g
performance and you can
buy it
for 30% off directly from the publisher.
|
Donald K. Burleson [info@remote-dba.net]
is one of the world's most widely-read Oracle database experts. He has written 19
books, published more than 100 articles in national magazines, and
serves as editor-in-chief of Oracle Internals, a leading Oracle
database journal. Burleson's latest book is
Creating a Self-Tuning Database
by Rampant TechPress. Don's Web sites are
http://www.dba-oracle.com ,
http://www.remote-dba.net/ and
http://rampant.cc .
|